Imbarcarsi sul idroponico Il viaggio può essere emozionante e travolgente, soprattutto di fronte alla miriade di scelte dei sistemi idroponici.
In questa esplorazione dei sistemi idroponici, sveliamo i misteri di sette tecniche distinte: Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Aeroponics, Drip System, Wick System, Vertical Hydroponics e Ebb & Sistema di flusso.
Ciascun metodo rappresenta un percorso unico per coltivare piante in un ambiente senza suolo e comprenderne le complessità può trasformare la complessità delle scelte in un'avventura elettrizzante.
Ciò che scegli non ha molta importanza, purché impari qualcosa qui e ti piaccia il processo. Dai, acquisire familiarità con i diversi modi di coltivare l'agricoltura idroponica renderà più semplice la navigazione nell'elenco dei sistemi idroponici.
Coltura delle acque profonde (DWC)
Rigogliosi sistemi radicali sospesi in una soluzione nutritiva: questo è DWC!
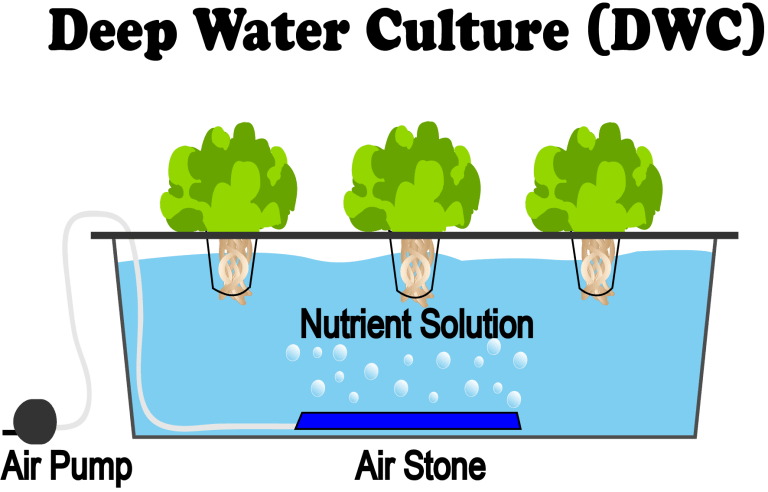
Principio di funzionamento del DWC:
Radici sommerse: le radici delle piante sono completamente immerse in una soluzione acquosa ricca di sostanze nutritive.
Piattaforma galleggiante o vaso in rete: le radici vengono spesso sospese nell'acqua utilizzando una piattaforma galleggiante o un vaso in rete, consentendo loro di accedere alla soluzione nutritiva.
Ossigenazione continua: l'ossigeno viene fornito alle radici attraverso pietre porose o diffusori che creano bolle nell'acqua.
Assorbimento dei nutrienti: le piante assorbono i nutrienti essenziali direttamente dall'acqua, promuovendo un efficiente assorbimento dei nutrienti.
Ambiente idroponico: DWC funziona come un sistema idroponico, eliminando la necessità di suolo e facendo affidamento sull'acqua per la distribuzione dei nutrienti.
Il sistema DWC è un sistema idroponico semplice e pratico adatto alla coltivazione domestica, agricola e commerciale.
Colture per DWC:
Verdure: lattuga, spinaci, cavoli, cetrioli, peperoni, pomodori,
Erbe aromatiche: basilico, menta, prezzemolo, coriandolo, ecc.,
Frutta: fragole, pomodori,
Fiori: calendule, convolvoli nani, ecc.,
Cannabis (dove legale).
Professionisti:
- Efficiente in termini di acqua e nutrienti, riduce il consumo di risorse idriche.
- Elevata efficienza dello spazio, adatta per coltivazioni su larga, media e piccola scala.
- Configurazione semplice, facile da mantenere.
- Resa elevata, crescita rapida.
Contro:
- Incline alla contaminazione dell'acqua, richiedono cambi regolari della soluzione.
- Le radici possono marcire facilmente, pertanto è necessario prestare attenzione alla temperatura dell'acqua e alla concentrazione della soluzione nutritiva.
- Scarsa mobilità, limitazione della flessibilità nei movimenti o riorganizzazione delle configurazioni.
- Suscettibile a guasti del sistema come interruzioni di corrente o malfunzionamenti delle apparecchiature.
Tecnica del film nutriente (NFT)
Le radici delle piante crescono in un sottile strato di soluzione nutritiva fluente: questo è NFT!
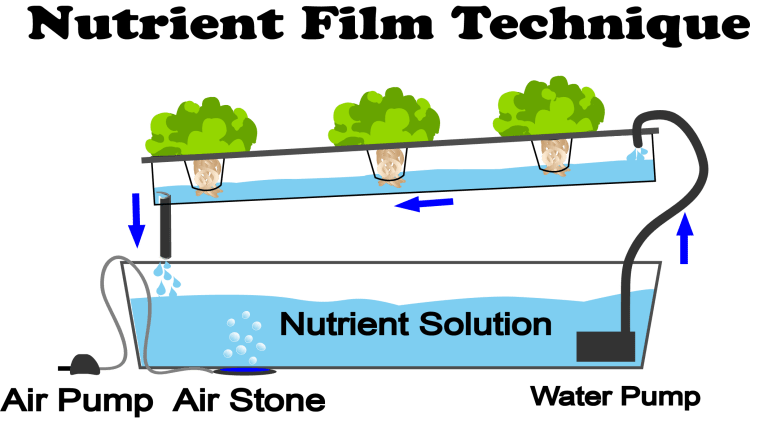
Principi di funzionamento dell'NFT:
Flusso continuo: un sottile film di acqua ricca di sostanze nutritive circola continuamente lungo un canale inclinato o una grondaia.
Esposizione delle radici: le radici delle piante sono sospese nella pellicola ed esposte a un flusso costante di sostanze nutritive e ossigeno.
Guidato dalla gravità: la pendenza del canale consente alla soluzione nutritiva di fluire sopra le radici per gravità.
Il sistema NFT è un sistema idroponico efficiente e a risparmio idrico adatto alla coltivazione domestica, agricola e commerciale. Il nostro sistema verticale, SG40, utilizza il sistema NFT per la semina.
Colture per NFT:
Verdura: Lattuga, spinaci, rucola, piccole varietà di peperoni;
Erbe aromatiche: erbe aromatiche, basilico, coriandolo, menta, prezzemolo, erba cipollina;
Altre colture: Microgreens, alcune varietà di cetrioli, alcune piante da fiore (a scopo ornamentale);
Bacche: fragole.
Professionisti:
- Soluzione nutritiva circolante sostenibile, efficiente in termini di acqua e nutrienti, che riduce il consumo di risorse idriche.
- Il design del sistema è tipicamente compatto e massimizza l’utilizzo dello spazio.
- Resa elevata, crescita rapida.
Contro:
- Elevata dipendenza dall'energia, contando su un'alimentazione continua per la pompa per mantenere il flusso della soluzione nutritiva.
- Non adatto a piante da frutto grandi o pesanti.
- Sistema complesso, che richiede monitoraggio e manutenzione regolari.
Aeroponica
In un sistema aeroponico, le radici delle piante sono direttamente esposte all'aria e la soluzione nutritiva viene spruzzata sotto forma di nebbia sulla superficie delle radici.

Principio di funzionamento dell'aeroponica:
Nebulizzazione delle radici: l'aeroponica sospende le radici delle piante nell'aria e fornisce i nutrienti attraverso una nebbia sottile o un aerosol.
Altamente ossigenato: le radici sono esposte ad alti livelli di ossigeno, favorendo un rapido assorbimento e crescita dei nutrienti.
Nebbia ricca di nutrienti: la soluzione nutritiva viene spruzzata direttamente sulle radici sotto forma di nebbia, massimizzando l'assorbimento dei nutrienti.
Utilizzo minimo di acqua: uso efficiente dell'acqua poiché viene applicata direttamente alle radici in modo controllato.
Il sistema aeroponico è un sistema idroponico efficiente e a risparmio idrico noto per la sua elevata resa. Le nostre torri idroponiche utilizzare il sistema aeroponico, molto apprezzato dagli agricoltori per coltivare una varietà di colture come verdure a foglia, erbe aromatiche e frutta.
Colture per Aeroponica:
Verdure a foglia: lattuga, spinaci, cavoli.
Erbe: basilico, coriandolo, menta.
Fragole: spesso coltivate in modo aeroponico per uno sviluppo ottimale dei frutti.
Microgreens: adatti per sistemi aeroponici.
Professionisti:
- Tassi di crescita elevati: rapida crescita delle piante grazie al maggiore assorbimento di ossigeno e sostanze nutritive.
- Efficienza idrica: utilizzo minimo di acqua rispetto alla tradizionale coltivazione del terreno.
- Controllo preciso dei nutrienti: consente un controllo preciso sulla concentrazione dei nutrienti, ottimizzando la salute delle piante.
- Efficienza spaziale: adatto per l'agricoltura verticale e ambienti con spazio limitato.
Contro:
- Complessità del sistema: richiede maggiori conoscenze tecniche per l'installazione e la manutenzione.
- Rischio di malfunzionamento del sistema: rischio di intasamento degli ugelli di nebulizzazione o di guasti alla pompa.
- Dipendenza dall'energia: l'alimentazione continua è fondamentale per il mantenimento dei cicli di nebulizzazione.
- Costo iniziale: costi di installazione iniziali più elevati rispetto ad altri metodi idroponici.
Coltura idroponica verticale
In un sistema idroponico verticale, le radici delle piante crescono in strati impilati verticalmente.

Concetto e principio di funzionamento:
Superfici di coltivazione verticale: utilizza strutture verticali per coltivare piante in strati o torri impilati.
Fornitura di nutrienti: l'acqua ricca di nutrienti viene fatta circolare o gocciola lungo la superficie verticale, fornendo alle piante elementi essenziali.
Flusso assistito dalla gravità: l'acqua scorre giù dalla parte superiore della struttura, sfruttando la gravità per raggiungere i livelli inferiori.
Letti di coltivazione impilati: le piante sono disposte in letti o torri impilati, ottimizzando lo spazio su un piano verticale.
I sistemi idroponici verticali sono adatti per la coltivazione domestica, agricola e commerciale.
Nostro sistema per giardino verticale SG40 è molto acclamato dagli utenti in vari campi. È particolarmente adatto per la ricerca educativa, l'educazione idroponica, la simulazione di fabbriche di piante, esposizioni commerciali e giardinaggio domestico.
Colture per la coltura idroponica verticale:
Verdure a foglia: lattuga, spinaci, cavoli, bietole, rucola;
Erbe aromatiche: erbe aromatiche, basilico, coriandolo, menta, prezzemolo;
Pomodori e peperoni: alcune varietà prosperano in condizioni di crescita verticale, soprattutto quelle con abitudini di crescita compatte;
Altre colture: microgreens, ravanelli, legumi e alcune piante da fiore a scopo ornamentale;
Professionisti:
- Massimizza l'uso di spazi limitati, adatti agli spazi urbani o confinati per la coltivazione;
- Rendimento elevato in una piccola area, aumento della densità di impianto e della produzione;
- Alto livello di automazione, riducendo i costi di manodopera;
- La disposizione verticale aumenta l'esposizione a fonti di luce artificiale o naturale;
Contro:
- Un sistema complesso richiede conoscenze specialistiche per la progettazione e la manutenzione;
- I costi iniziali durante l'implementazione possono essere elevati, soprattutto per i sistemi di automazione;
- Garantire una distribuzione uniforme dei nutrienti su ogni strato può essere difficile.
Sistema a goccia
Le radici delle piante ricevono la soluzione nutritiva attraverso un sistema di irrigazione a goccia: questo è il Drip System!
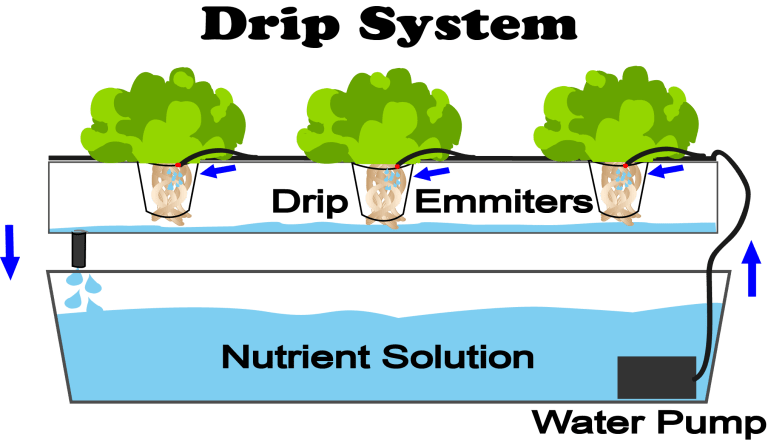
Principio di funzionamento:
Gocciolamento per pianta individuale: la soluzione nutritiva viene erogata direttamente a ciascuna pianta attraverso gocciolatori individuali.
Intervalli regolari: il sistema funziona con un timer, fornendo gocciolamenti controllati e periodici della soluzione nutritiva.
Ricircolo: la soluzione nutritiva in eccesso non assorbita dalle piante viene raccolta e rimessa in circolo attraverso il sistema.
I sistemi a goccia sono adatti per la coltivazione domestica, agricola e commerciale.
Colture per Sistema a Goccia:
Verdura: Pomodori, peperoni, cetrioli, zucchine, lattuga, spinaci, broccoli;
Frutta: fragole, mirtilli, meloni (come anguria e melone);
Erbe aromatiche: basilico, timo, origano, rosmarino, menta, coriandolo;
Altre colture: fiori (come rose, margherite africane, convolvoli nani), piselli.
Professionisti:
- Risparmio idrico, riduzione del consumo complessivo di acqua.
- Aumento della resa, consentendo la coltivazione di più raccolti.
- Elevati livelli di automazione, con conseguente riduzione dei costi di manodopera.
- Facile da espandere, offre flessibilità nel ridimensionare il sistema.
- Adatto a una varietà di colture, versatile nell'applicazione.
Contro:
- Le teste di irrigazione a goccia possono essere soggette a intasamenti a causa dell’accumulo di sedimenti o della precipitazione di nutrienti.
- Qualsiasi interruzione di corrente può causare interruzioni del sistema.
- L’installazione di un sistema di irrigazione a goccia può richiedere conoscenze tecniche.
- È necessaria cautela per evitare un'irrigazione eccessiva, soprattutto in situazioni con portate elevate o durate prolungate.
Sistema stoppino
Le radici delle piante crescono nel cotone che assorbe l'acqua e la soluzione nutritiva viene convogliata alle radici attraverso il cotone che assorbe l'acqua: questo è il sistema Wick!
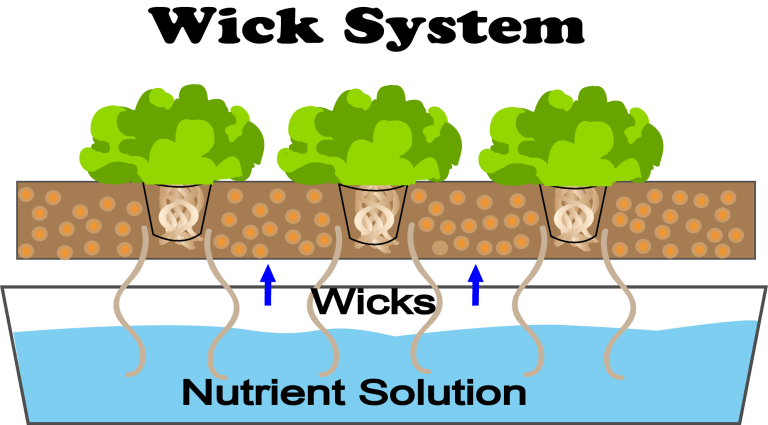
Principio di funzionamento:
Azione capillare: si basa sull'azione capillare attraverso stoppini (solitamente realizzati in feltro o altri materiali assorbenti) per fornire la soluzione nutritiva alle radici delle piante.
Movimento passivo: la soluzione nutritiva si sposta da un serbatoio attraverso stoppini al terreno di coltura dove le radici delle piante la assorbono.
Umidità continua: mantiene un livello costante di umidità nel terreno di coltura.
Questo metodo non richiede pompe dell'acqua o altre attrezzature, il che lo rende adatto al giardinaggio domestico.
Colture per il sistema Wick:
Erbe aromatiche: basilico, menta, coriandolo, prezzemolo, erba cipollina;
Verdure a foglia: lattuga, spinaci, cavoli, bietole;
Fragole: adatte per varietà di fragole più piccole;
Altre colture: piccole piante da fiore, piante domestiche in vaso a bassa manutenzione.
Professionisti:
- Facile da installare e utilizzare, ideale per i principianti idroponici.
- Richiede attrezzature minime, a basso costo, adatte al giardinaggio domestico.
- Non necessita di elettricità, funziona passivamente senza pompe dell'acqua o componenti elettrici.
- Design compatto, ideale per il giardinaggio su piccola scala o indoor.
Contro:
- Resa bassa, adatta alla coltivazione di piccole colture, non adatta a piante da frutto grandi o pesanti.
- Il lento assorbimento dei nutrienti e l’azione capillare possono portare a un assorbimento più lento dei nutrienti.
- Potrebbe verificarsi una distribuzione non uniforme dei nutrienti nel terreno di coltura.
- Rischio di irrigazione eccessiva, che può influire sulla salute delle radici in determinate situazioni.
Sistema di flusso e riflusso
In questo sistema, le radici delle piante crescono in un terreno di coltura e la soluzione nutritiva viene fatta circolare nel letto di coltivazione attraverso una pompa dell'acqua prima di essere nuovamente drenata.

Principio di funzionamento:
Inondazioni e drenaggi periodici: la soluzione nutritiva inonda periodicamente il terreno di coltura e poi drena nuovamente in un serbatoio.
Pompa sommergibile: una pompa sommergibile viene utilizzata per allagare il letto di coltivazione e una pompa di drenaggio rimuove la soluzione in eccesso.
Cicli temporizzati: funziona su cicli temporizzati, con intervalli di allagamento e scarico controllati da un timer.
Il sistema di flusso e riflusso è adatto per la coltivazione domestica, agricola e commerciale.
Colture per Riflusso & Sistema di flusso:
Verdure: Pomodori, Peperoni, Cetrioli, Lattuga, Spinaci.
Erbe aromatiche: basilico, coriandolo, menta, prezzemolo.
Fiori: rose, gerbere, petunie.
Frutta: fragole, meloni.
Professionisti:
- L'irrigazione regolare garantisce un apporto e un assorbimento ottimali dei nutrienti da parte delle piante.
- Adatto a vari tipi di piante, soddisfacendo le esigenze di diverse colture.
- I cicli di allagamento e drenaggio, rispetto ai sistemi a flusso continuo, riducono il rischio di irrigazione eccessiva.
Contro:
- Dipendenza dall'elettricità, che richiede energia per azionare pompe sommergibili e di drenaggio.
- Più complessi dei sistemi passivi, richiedono un'attenta installazione e manutenzione.
- I guasti alle pompe possono interrompere i cicli di allagamento e drenaggio.
- Richiede uno spazio più ampio e in determinate situazioni potrebbe non essere efficiente in termini di spazio come i sistemi più piccoli.
Jayes
In qualità di responsabile del marketing digitale presso AUXGROW, Jayes unisce la passione per i sistemi idroponici e l'esperienza nelle luci di coltivazione a LED. Con esperienza pratica e profonda comprensione, Jayes ti guida attraverso il mondo della coltivazione sostenibile.






